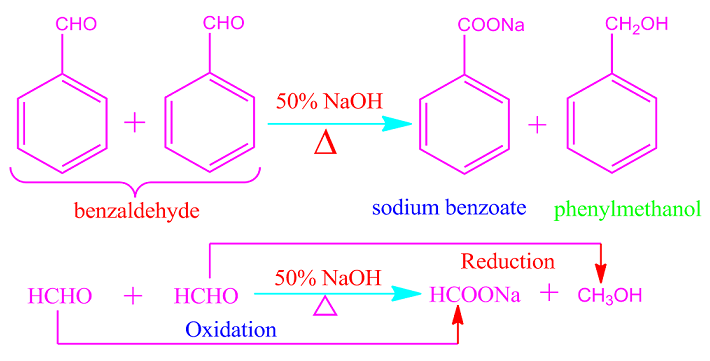
What is
Cannizzaro reaction?
Aldehydes that do not have an
alpha hydrogen atom undergo auto-oxidation reduction reactions when heated with
concentrated or 50% NaOH or KOH solutions.
That is, half of the
participating aldehydes molecules are oxidized to carboxylic acids (as sodium
or potassium salt) and half are oxidized to alcohols. This
auto-oxidation-reduction reaction is called Cannizzaro reaction. Cannizzaro
reaction is also called disproportionation reaction.
Formaldehyde, trimethylacetaldehyde, benzaldehyde or any other aromatic aldehydes participates in the Cannizzaro reaction because of the absence of alpha hydrogen.


.jpg)