Oxidation agent definition with examples in chemistry
In a chemical reaction, if a substance oxidizes another
substance but reducing itself then it is called an oxidation agent or oxidant.
The
oxidation agent or oxidant oxidizes
the other substance by rejecting the electrons, and accepting those electrons
be reduced by itself.
For
examples, fluorine (F2), chlorine (Cl2), oxygen (O2), ozone (O3), potassium
permanganate (KMnO4), potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) etc.
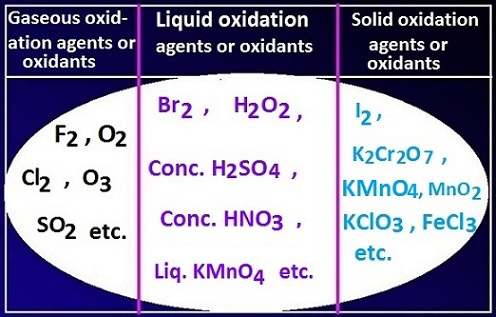
What are the various types of oxidation agent?
There
can be three types of oxidation agent
or oxidant depending on the state of matter, such as solid oxidation agents,
liquid oxidation agents, and gaseous oxidation agents.
Depending
on the strength, there are another two types of oxidation agent or oxidant, such as strong oxidation agent and weak or mild oxidation agent.
Oxidation agent examples list
What is strong oxidation agent in chemistry?
The
strength of oxidation agent or
oxidant depends on their standard reduction potential determined at 298 K
temperature.
Oxidants that have a high standard reduction potential value are
called stronger oxidation agent.
For examples, fluorine (+2.87 volt), permanganate ion
(+1.78 volt) etc are act as strong oxidation
agent.
What is weak or mild oxidation agent?
Oxidants that have a lower standard reduction potential value are
called weaker or mild oxidation agent.
For examples, iodine (+0.54 volt), stannic chloride (+0.15
volt) etc are act as weak or mild oxidation
agent.
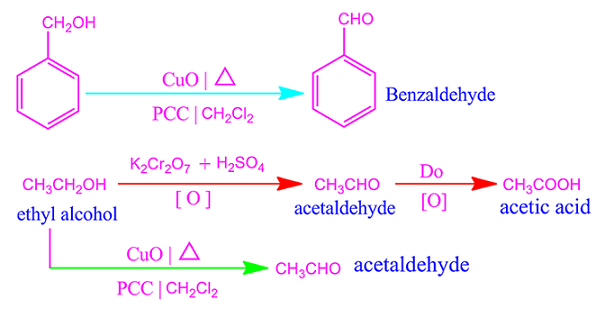
Oxidation agent in organic chemistry
There
are various oxidation agents or
oxidants of both strong and weak are used in organic chemistry.
These
oxidation agents or oxidants are
used for the purpose of oxidation reaction of different organic compounds such
as alcohol, aldehyde, ketone, ester, alkane, alkene, amine etc.
For
example, strong oxidation agent
potassium dichromate and concentrated sulfuric acid oxidized alcohol to
carboxylic acid directly.
Again,
weak or mild oxidation agent
pyridinium chlorochromate or PCC oxidized alcohol to aldehyde. This oxidation
process is limited to aldehyde levels.
What is CO oxidation in surface chemistry?
CO oxidation is related to
surface chemistry. Because CO oxidation
occurs on the surface of the catalyst, i.e. CO oxidation occurs in the presence of a catalyst.
Thus CO
oxidation can be of two types depending on the phase of the reactant,
catalyst and product, namely, homogeneous catalysis process and
heterogeneous catalysis process.
If the reactant, the catalyst and the product
are in the same phase, then that catalysis is called homogeneous catalysis.
On the other hand, if the reactant, the catalyst and the
product are in the different phase, then that catalysis is called heterogeneous
catalysis.
Such as, catalytic CO oxidation
clears emissions from motor vehicle and industrial smoke stacks. In this case solid Pt is used as a catalyst.
So it is a heterogeneous catalysis process.
The
reaction follows complex mechanism. In this case two types of CO2 molecules are
formed, hyper thermal and thermal.
Again,
in the presence of nitric oxide gas, carbon dioxide is produced by the reaction
of carbon monoxide and oxygen gas. It is an example of a homogeneous catalysis
involving CO oxidation.
This
is because in this process the reactants, catalysts and products remain in the
same phase. In this case NO gas acts as a
catalyst.
During
the formation of photochemical smog, CO is oxidized by oxygen in the air in the
presence of sunlight to form carbon dioxide and ozone.
So
this is also an example of a CO oxidation
process. The reaction occurs through free radical formation.
It
has been also found that CO can be oxidized by water. The reaction of water with
CO produces carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The reaction is very slow.
However,
when the partial pressure of hydrogen in this reaction is high, HCOOH is
produced in the reaction of water with CO. It
is also an example of a CO oxidation
process.
- Oxidation agent definition with examples in chemistry
- What is CO oxidation in surface chemistry?
- Oxidation agent examples list
- What are the various types of oxidation agent?
- What is strong oxidation agent in chemistry?
- What is weak or mild oxidation agent?
- Oxidation agent in organic chemistry
Oxidation
agent, oxidation agent definition, CO oxidation, carbon monoxide oxidation, oxidation
agent meaning, best oxidation agent, oxidation agent examples list, oxidation
agent in organic chemistry, strong oxidation agent, weak or mild oxidation
agent, definition of oxidation agent, oxidation agent strength,
Read more : Uses of carbon dioxide in environment













No comments:
Post a Comment