Why is Cu+ diamagnetic while Cu2+ is paramagnetic?
The
diamagnetic and paramagnetic character of a substance depends on the number of odd electron present in that substance. The diamagnetic and paramagnetic
character of Cu+ and Cu+ are discussed below.
Now,
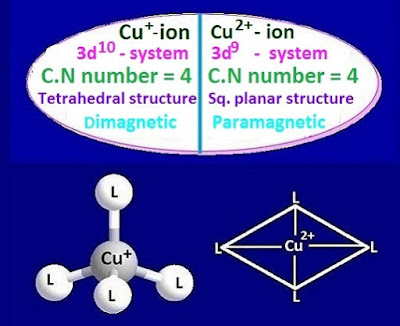
depending upon the hybridization, there are two types of possible structure of Cu+
and Cu2+ ion are formed with co-ordinationnumber 4.
If
the complex ion involves ‘sp3’ hybridization, it would have tetrahedral
structure. Again, if the complex involves ‘dsp2’ hybridization, it would have
square planar structure.
According
to Hund’s rule the outer electronic configuration of Cu+ ion is [Ar] 3d10
that is
Cu+
ion is 3d10 systems. That
is, 3d orbital of Cu+ ion is completely fulfilled but outer 4s orbital is
vacant.
Hence
according to valence bond theory the outer ‘4s’ orbital of cu+ ion is combined
with the vacant three 4p orbital and form energetically equivalent four
hybridized orbitals.
They
are called sp3 hybridized orbitals. Now, four similar or dissimilar ligands are attached with these four hybridized orbitals through the formation of four
co-ordinate bond.
As
a result, Cu+ ion forms tetrahedral
molecule involving ‘sp3’
hybridization. The outer electronic configuration of Cu+ ion and
its hybridization are shown below.
From
the above electronic configuration of Cu+ ion, it has been found that it has no
unpaired electrons. Since the Cu+ ion has no unpaired electrons, hence it is diamagnetic.
On
the other hand, Cu2+ions are 3d9
system. According to Hund’s rule, the outer electronic configuration of Cu2+ion
is [Ar] 3d9 system.
From the above electronic configuration of Cu2+ion,
it has been found that four d-orbitals of 3d-subshell is occupied by paired
electrons and rest of the 3d-orbital contained single electron.
Now in the excited state the single electron of 3dx2-y2
orbital absorbs energy and shifted to vacant 4Pz orbital. As a result of this,
the inner 3dx2-y2 orbital become vacant.
Under this condition, the vacant orbital of inner
3d-orbital is attached with the outer one 4s and 4p-orbitals, resulting in the
formation of four energetically equivalent orbitals involving dsp2
hybridization.
Now, these four energetically equivalent vacant
orbitals are chemically attached with four ligands through the formation of
ligand-metal co-ordinate bond involving square planar structure molecule.
Under this
condition, Cu2+ion have one unpaired 4Pz electron. Hence Cu2+ion
show paramagnetic properties.
The outer electronic configuration of Cu2+ion
and its hybridization are shown below.
- Why is Cu+ diamagnetic while Cu2+ is paramagnetic?
- Why is Cu2+ paramagnetic whereas Cu+ is diamagnetic?
- Why is Cu+ ion diamagnetic in nature?
- Why is Cu2+ ion paramagnetic in nature?
Cu+ ion diamagnetic while Cu2+ ion is paramagnetic, Cu+
ion diamagnetic, Cu2+ ion paramagnetic, Cu2+ ion paramagnetic whereas Cu+ ion
is diamagnetic,
Read more : Different types of air pollution and their sources.











No comments:
Post a Comment