Ligand definition in co-ordination chemistry
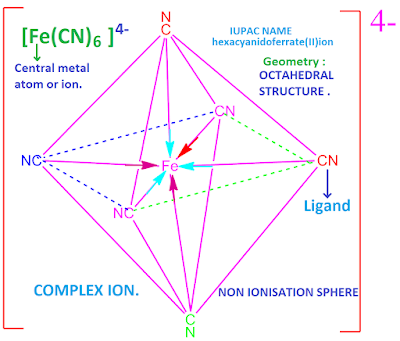
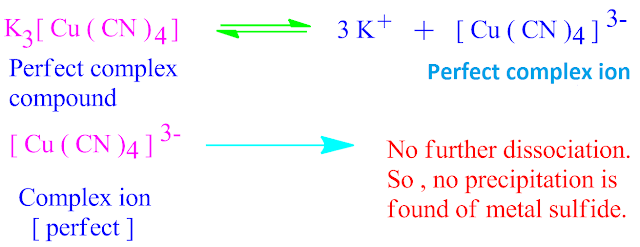
In co-ordination chemistry, the cation to which one or more neutral molecules or ions are co-ordinated is called centralmetal cation, while the molecules or ions so attached are called Ligand.
For examples , CN– , Cl– , CO
, H2O NH2–NH2
etc.
Ligand examples in co-ordination chemistry
There are three types of ligands depending on the nature of charge are known . Such as cationic ligand, anionic ligand and neutral ligand.
Ligand types in co-ordination chemistry
There are different types of ligands are known depending on their function in co-ordination with the central metal ion in co-ordinationchemistry .
Such as ambident
ligands , flexidentate ligands , classical ligands, non-classical ligands,
chelating ligand, π-acid ligand etc.
Ambident ligands.
There are
few ligands which contain more than one donor atom, but they can use only one
donor atom at once in the formation of complex compound, these type of ligands
are called Ambident ligands.
There are two types of ambident ligand, namely, mono dentate ambident ligand and bidentate ambident ligand.
When a mono
dentate ambident ligand ( such as nitrite ion ) ,is attached with different
central metal ion , it uses either ‘N’ atom or ‘ O ‘ atom as a donor atom .
Similarly, when a bidentate ambident ligand ( such as dithio oxalate ion ), is attached
with different central metal ion, it uses either both the ‘O’ atom or both the
‘S ‘ atom together as a donor atom.
Flexidentate ligands
There are
few ligands in co-ordination chemistry which have two or more donor atoms.
But ,they do not use their entire donor atom at once in the formation of co-ordination compound that is in co-ordination with central metal ion .
They use
their different donor atom with different metal ion to form co-ordinate bond .
Such types of ligands are called flexi dentate ligands.
For example,
Cysteine, a tri-dentate ligand with three different donor atoms ( S, N, O )
act as a di dentate ligand in three different way [ when it uses S,N , N,O
and S,O atom separately ]
So, Cysteine
is a flexi dentate ligand.
Similarly,
there are many other poly dentate ligands those are behaved as a flexi dentate ligand.
Such as,
EDTA , a poly dentate ligand , but in some cases it uses as a penta dentate or
tetra dentate ligand. So, EDTA is also a flexi dentate ligand.
There are
another two types of ligands are known which are, classical ligands and
non-classical ligands .
( I ) Classical ligands : Classical ligands are those ligands which can
co-ordinate with the central metal ion by using their lone pair of electrons .
For examples
CO , CN – , F –, Cl – , OH –,
H2O , NH3 etc .
(II ) Non-classical ligands : There are few
ligands which uses their electron-pair of pi bond in the formation of
co-ordinate bond with the central metal ion , these type of ligands are called Non-classical ligands.
For examples C2H4 , C6H6
, C5H5 – [ cyclo penta dienyl anion ] etc.
Summary :
- Ligand definition in co-ordination chemistry
- Ligand examples in co-ordination chemistry
- Ligand types in co-ordination chemistry
- What is ambidentate ligands ?
- What is flexidentate ligands ?
- What is classical ligands ?
- What is non-classical ligands ?