· activating groups explain with an example
Activating
groups
are some chemical constituents which increase the electron
density of benzene
ring owing to their positive mesomeric effect and inductive effect.
In
other words, there are some groups in organic chemistry, which have electron
donating ability and they can activate the benzene ring through increasing the
electron density of benzene ring, are called activating groups.
Since
these type of groups activate the benzene ring, so they are called activator
enhancer or activating groups. Activating
groups
are also called electron donating group.
Most
of the activating groups contain one
or more lone pair of electron.This
lone pair of electron participate in resonance with the pi electron of benzene
ring.
As
a result, benzene ring with activating groups become electron rich.That
is, benzene ring acts as a source of electrons.
Therefore,
benzene ring with activating group becomes more reactive towards electrophilic
substitution reaction than benzene ring without activating groups.
·
Activating
groups list.
There
are three types of activating groups
are known in organic chemistry, namely, strong activating groups, medium activating
groups and weak activating groups.
Activating
groups
list of these three type are shown below.
·
Why are activating groups
also called ortho, para directing
groups ?
Activating
groups
increase the electron density of benzene ring due to their +I and +M effect.
It
has been found that, owing to presence of activating
groups, the density of electron increase basically, on the ortho and para
carbon atom of the ring.
So,
in electrophilic substitutionreaction, the electrophile attack on ortho and para carbon atom only.
Hence, activating
groups which are already present in the benzene ring, indicate the incoming
group to take the ortho and para position of the ring.
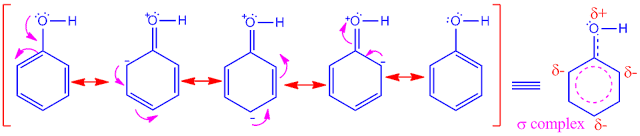
For
example, nitration of phenol gives ortho and para nitro phenol.
That
is, the –OH group of phenol which
already exist in benzene ring , is ortho
and para directing.
Similarly,
chlorination of toluene, gives ortho and para chloro toluene . So, –CH3 group is also a ortho and para directing group.
Although,
in both cases, para product is predominant than ortho product, due to steric hindrance in ortho position.
For
the above reason, activating groups are
also called ortho, para directing
groups.
·
deactivating
groups explain with an example
Deactivating
groupsare those groups which decrease the electron density of benzene ring owing to
their –I effect as well as –M effect.
In
other words, there are some groups in organic chemistry, which have electron
accepting ability and they deactivate the
benzene ring through reducing the
electron density of benzene ring, are called deactivating groups.
Since
these type of groups deactivate the benzene ring, so they are called activator
reducer or deactivating groups.
Deactivating
groups
are also called electron withdrawing
group.
·
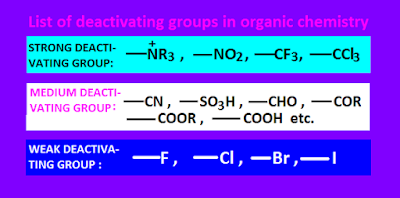
Deactivating
groups list.
There
are three types of deactivating groups
are known in organic chemistry,
namely, strong deactivating groups,
medium deactivating groups and weak deactivating groups.
Dectivating groups list of these three type are shown below.
Dectivating groups list of these three type are shown below.
·
Why are
deactivating groups also called meta-directing groups ?
Deactivating
groups
are also called electron with drawing
groups.
The
– I effect of deactivating groups
reduce the electron density from all the position of benzene ring.
But,
owing to –R effect of deactivating group,
the electron density reduces, basically from ortho and para position.
So,
the density of electron at meta position
remain comparatively more than ortho and para position.
Hence,
in electrophilic substitution
reaction, the electrophile attack on meta position only.
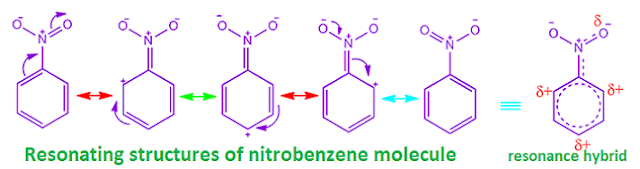
For
example, nitration of benzaldehyde gives meta nitro benzaldehyde.
That
is, the –CHO group of benzaldehyde which already exist in benzene ring , is
meta directing.
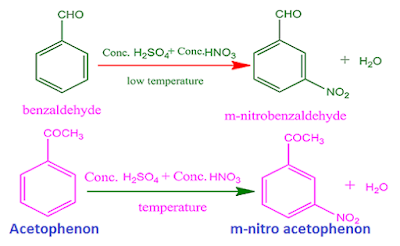
Similarly,
nitration of acetophenon, gives meta nitro acetophenon. So, –COCH3 group is also a meta directing group.
For
the above reason, deactivating groups
also called meta-directing groups.
· activating groups in aromatic electrophilic substitution.
·
activating groups explain with an example
·
Activating and deactivating groups list.
·
Why are activating groups also called ortho,para directing groups ?
·
Why are deactivating groups also called
meta-directing groups ?











No comments:
Post a Comment