Ionic bond definition in chemistry
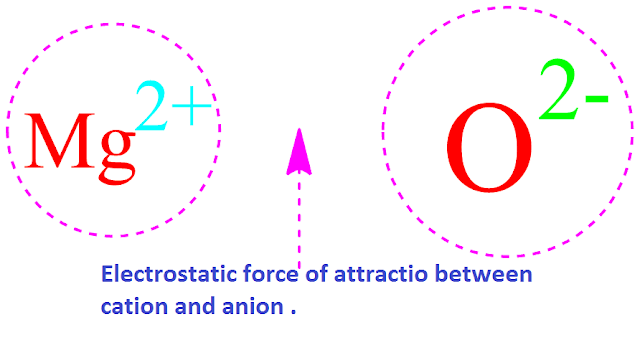
Ionic bond or electro-valent bond is one type of chemical bond which is formed by the force of electrostatic attraction between cation and anion .
Actually,
ionic bond is nothing but electrostatic force of attraction between the
opposite ions .
What is ionic valency ?
Most of the
elements have a tendency to gain more stable electronic configuration like
their nearest inert gas elements .
So, one or
more electrons from outer most shell of an electro-positive atom is completely
transformed to the outer most shell of the electro-negative atom, resulting in
the formation of stable cation and anion .
Then, they
formed a compound by the electrostatic force of attraction .
The power ofcation and anion, through which they exhibits their ability to form a compound
, is called electro-valency or ionic valency .
Examples of ionic compounds
There are a
large number of well known ionic compounds in the world. Few examples are , NaF
, MgO , KCl , CsCl CaCl2 etc .
Condition for the formation of ionic compounds
( I )In case
of ionic bond formation, one of the participating element must be
electro-positive and the other should be electro-negative.
That is ,
the difference of electronegativity between the concern two elements must be
sufficient .
( II )The
number of valence electron of electro-positive element should be 1 ,2 or 3 and that of electro-negative element
must be 5 , 6 or 7 respectively .
( III )The
size of the electro-positive element should be small and the size of the
electro-negative element should be large .
( IV )The
electron affinity as well as ionization energy of the participatingelectro-positive element should be small so that cation is formed very easily.
But the
electron affinity value of the concern electro-negative element must be high so
that , it can gain electron to form anion easily.
( V )The
extent of charge on both the cation and anion should be less so that they
exhibit less tendency to regain their leaving electron.
( VI )If the
amount of energy released due to formation of ionic bond is so much high , then
the formation of electro-valent or ionic compound becomes more favorable.
Properties of electro-valent or ionic compounds.
( I )
Actually, there is no existence of ionic bond or ionic molecule . In ionic
compounds, the ions with opposite charge form an three dimensional ionic
crystal.
( II ) Since, ionic bond is nothing but
electrostatic force of attraction between cation and anion , so boiling point
and melting point of ionic compound is high with compare to the other compounds.
( III )
Since ions have no direction, hence ionic bond have no direction . That is,
ionic valency is non directional .
( IV ) The
ionic compounds are ionizable. They ionized in aqueous solution or in melting
condition. So they are good conductors of electricity.
( V ) Since ionic bond have no specific
direction , so ionic compounds do not exhibit isomerism properties .
(VI ) Ionic
compounds are generally polar. Hence they are soluble in polar solvent like
water. But they are insoluble in non-polar solvent ( CCl4 , CS2, C6H6 etc ).
( VII ) The rate of reaction among the ionic
compounds are very much high .
( VIII ) The ionic compounds with equal
electronic arrangement but different ion show integrated properties . For
example , NaF and MgO .
Summary :
Ionic bond definition in chemistry .
What is ionic valency ?
Example of ionic compounds .
Properties of electro-valent or ionic compounds.
Condition for the formation of ionic bond .










Valuable information.unique content.Thanks for sharing.
ReplyDeleteSelenium Training in chennai | Selenium Training in anna nagar | Selenium Training in omr | Selenium Training in porur | Selenium Training in tambaram | Selenium Training in velachery
Thank you for your support.
DeleteThank you for your comments.
ReplyDelete