What is tricyclohexylphosphine in organic chemistry?
Tricyclohexylphosphine
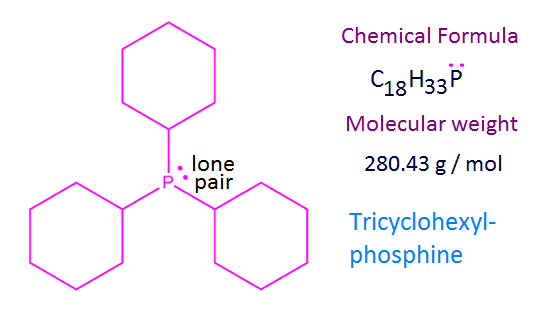
is a tertiary phosphine with chemical formula C18H33P. It
is also expressed with the formula P(C6H11)3
or P(Cy)3, where Cy stands for cyclohexyl group.
Tricyclohexylphosphine
is formed by the substitution of three hydrogen atoms by three cyclohexyl
group.
The molecular weight of Tricyclohexylphosphine is 280.43 g / mol and its melting point is 355K. Tricyclohexylphosphine is soluble in organic solvents.
Tricyclohexylphosphine is commonly used as a ligand in
organometallic chemistry. It is characterized by both high basicity and a large
ligand cone angle.
Why
is tricyclohexylphosphine highly basic?
The phosphorous atom in tricyclohexylphosphine is sp3 hybridized. The phosphorous atom
contains one lone pair of electron which can’t participate in resonance with
cyclohexyl ring due to absent of pi bond in cyclohexyl ring.
Hence the lone pair on phosphorous atom is available for donation to the electron deficient groups, atoms or ions. Consequently tricyclohexylphosphine shows high basic character.
Use of tricyclohexylphosphine
The central phosphorous atom in tricyclohexylphosphine
contains one lone pair of electron which is available for donation. Hence
phosphorous atom can co-ordinate with the other electron deficient species by
using its lone pair.
Due to such properties tricyclohexylphosphine is mainly used as a ligand in organometallic
chemistry.
- What is tricyclohexylphosphine in organic chemistry?
- Why is tricyclohexylphosphine highly basic?
- Use of tricyclohexylphosphine
Phosphine-tricyclohexylphosphine-tricyclohexylphosphine
highly basic-use of tricyclohexylphosphine










No comments:
Post a Comment