Why are most transition metals used as catalysts?
Most of the transition metals and their compounds are
used as catalyst in the chemical reaction. They are known for their homogeneous
and heterogeneous catalytic activity.
Transition metal elements exhibit catalytic property
because of their some special characters those are given below.
·
Transition metals have vacant d-orbitals.
·
They have a tendency to exhibit variable
oxidation states. The first transition series metals utilize 3d and 4s
electrons for bonding. Similarly second and third transition series metals utilize 4d, 5s and 5d, 6s electrons respectively.
·
Transition metals have a tendency to form
intermediate compound with reactants.
·
The presence of defects in their crystal
lattices.
·
Transition metal elements
have a larger surface area which is important character of transition metals
and it eligible them to be used as catalyst.
This is because one or more
reactant molecules are absorbed on the surface of the metal (catalyst) due to
the free valency of the atoms of the metal present on the surface.
This increases the concentration of the reactant on the surface
of the metal catalyst. As a result, the desired reaction is easily
accomplished.
There are some important or
well-known transition metals and their compounds that are used as catalysts in
various chemical reactions.
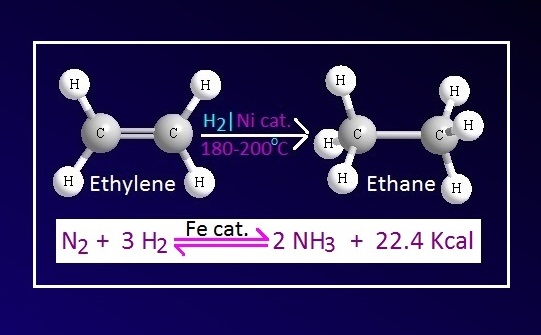
For example, Fe is used as
catalyst in the industrial production of ammonia in Haber process. In the
reaction Mo is used as promoter.
Pt or V2O5 is used as
catalyst in the contact process for the preparation of sulfur trioxide from
sulfur dioxide by oxidation.
Most important and familiar
catalyst is MnO2. Manganese dioxide catalyst is used in the laboratory
preparation of oxygen by heating potassium chlorate at low temperature.
Besides, in organic
reaction many transition metals and their compounds are used as catalyst. For
example, Ni catalyst is used in the hydrogenation process of oil and fat.
Again, in the preparation
of aldehyde by hydrogenation of acid chloride, Pd metal and BaSO4 are used as
catalyst in the presence of quinoline.
In polymer chemistry, TiCl4
which is also known as Zeigler-Natta catalyst is used in the preparation of
polythene from ethylene.
Mechanism of catalysis of transition metals
(I)The atom of a transition
metal element has more than one unpaired electron in their partially filled
d-sub-shell.
This is why the atoms of the transition element are able to absorb different amounts of energy and release that absorbed energy if necessary.
For this feature, the
transition metal elements are able to supply the activating energy required for
the chemical reaction.
(II)Due to the presence
of d-electrons in the atoms of the transition elements, they can react with
reactive molecules at different oxidation levels to form various types of
temporary intermediate compounds.
Thus lower activation energy
accelerates the chemical reactions through powerful alternative reaction
pathways.
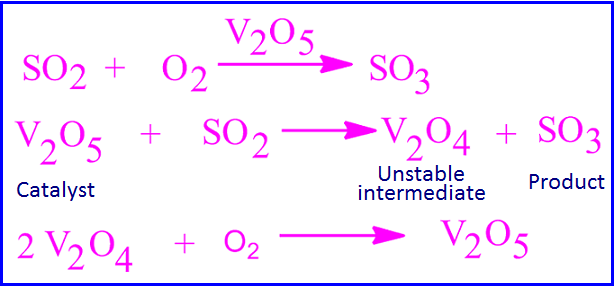
Reaction mechanism of SO2 to SO3 change
V2O5 is used as catalyst in
the contact process for the preparation of SO3 from SO2 by oxidation. The
reaction takes place in two steps.
In the first step, V2O5 is
reacts with SO2 to form SO3 and V2O4. In the second step, V2O4 is reacts with
oxygen and again V2O5 obtained.
In this reaction, the
oxidation number of vanadium first decreases from +5 to +4 and then again
increases from +4 to +5.
- Why are most transition metals used as catalysts?
- Mechanism of catalysis of transition metals
- Why nickel metal used as good catalyst?
transition metals used as catalysts, mechanism
of catalysis of transition metals









No comments:
Post a Comment