Acid rain definition in environmental chemistry
Acid
rain is one type of rain or any other form of precipitation with acidic
components [HNO3, H2SO4, HCl, H2CO3,
HNO2 etc] that fall to the ground from the atmosphere with rain
water.
When
some non metallic acidic oxide such as SO2, NO2, HCl etc
gaseous substances are mixed with dew, snowfall and rain water, forming
sulfuric acid, nitric acid and hydrogen chloride come down on the earth from
atmosphere, then this phenomenon is called acid rain.
The effect of acid rain is less in India. The
incidence of acid rain is highest in European countries, United state, Canada,
china etc.
Because, acid rain is directly related to the airpollution and the level of pollution is highest in these countries.
In the United States, about 70% of sulfur dioxide pollution
comes from power plants and about 40% of NO2 enter the atmosphere
from motor vehicles emitting with many other sources.
In Canada, about 60% of sulfur dioxide pollution comes from
industrial activities including oil refining and metal smelting.
Again, about 55%-60% of
NO2 gas enters into the air from motor vehicles emitting and many
other sources.The above said air polluting gases are responsible for
acid rain.
What are the sources of acid rain in environment?
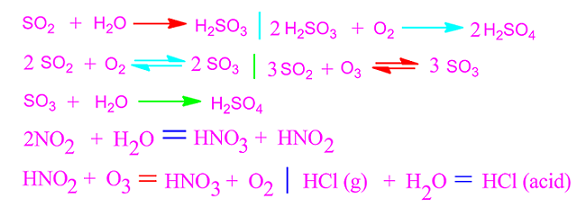
The gases responsible for acid rain are sulfur dioxide
(SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), hydrogen chloride (HCl)
etc.
These gases enter into the atmosphere for various
reasons. There are some natural causes and some man-made reasons.
Natural causes are forest fire, volcanic eruptions etc
through which a tiny part of SO2, NO2 enter into air.
But a huge amount of SO2, NO2 and
HCl gas enter into the air due to man-made reason.
A large extent of SO2, NO2 gases
enter into atmosphere from acid production industry, oil refineries, thermals
power station and from motor vehicle fumes.
Besides, NO2 oxide is formed by the reaction
of atmospheric N2 and O2 at the time of lightning. Again, some extent of hydrogen
chloride gases from HCl acid producing industries enter into the air.
These gases combine with rain water and fall to
the earth surface in the form of acid rain.
What is the contribution of different acids in acid rain?
In the creation of acid rain, the contribution of
sulfuric acid is 60-65% and that of for nitric acid is 30-35%. The other acids
those are responsible for acid rains are HCl, H2SO3 and
HNO2 etc.
What is the pH value of acid rain?
The natural rain water is mildly acidic with pH value
5.6 as some portion of atmospheric CO2 is mixed with natural rain
water in the form of carbonic acid.
But the pH range of acid rain is 5.6 – 3.5. The high
acidic nature of acid rain is due to presence of HNO3, H2SO4
and HCl acid.
These acids are formed when some gaseous chemicals of
atmosphere such as, SO2, NO2 and HCl etc are combined
with rain water and drops on the earth as acid rain.
What are the consequences of acid rain in environment?
Acid rain has a harmful effect on animal’s world as
well as on plants world due to its corrosive nature.
It has a fatal impact on soil, aquatic environment,
forest public health, historically architecture, monument etc.
The harmful
effects of acid rain on environment are discussed below.
Effect of acid rain on soil
The acidic nature of soil increases due to acid rain. Since,
the acidity of soil increases, hence the solubility of inorganic salts of soil
are changed.
As a result of acid rain, the pH value of soil changes
that prevents the ionic change in soil.
For this reason, sensitive soil microorganism that
can’t adapt with this pH changed. Hence, they are affected seriously or killed.
Effect of acid rain on forest and wild life
Acid rain affects a wide spread forest sometimes
partially or completely.
Since, acid rain drop on leaves of tree, hence it can
damage the leaves entirely. As a result, photosynthesis process on green leave
does not occur and hence trees can’t produce food.
Again, acid rain increases the acidity of soil. So,
taking of foods from soil becomes problematic for plants.
Hence, the prevention power of plats, against disease gradually
decreases. Normally, the entire plant world has to face losses.
Acid rain is also affects the wild life directly as
well as indirectly. Many wild animals die instantly as a result of acid rain.
Again, acid rain damages the entire forest. Hence, wild
life has to face lack of food. They suffer from lack of safe shelter.
Effect of acid rain on aquatic environment
Acid rain has a baneful effect on aquatic environment
along with a indirect effect on human health.
The aquatic animals and plants survive in a specific pH
value. Now, due to acid rain, the pH value falls below the specific level of
aquatic environment.
As a result, the aquatic animals accept death. Besides,
lower pH value can also kill adult fish through which the indirect effect of
lower pH value falls upon human health.
Effect of acid rain on architecture and sculpture
Acid rain has a harmful effect on man-made building,
architecture, sculpture, metal pipe etc.
Acid rain can damage these architecture or sculpture
partially or some time completely.
Architecture or sculpture those are constructed by lime
stone, react with mineral acid of acid rain and hence erosion is obtained.
For example, there are many historical monument, sculpture
in India, such as Taj mahal, Victoria, Lalkila etc are severely affected by
acid rain.
Effect of acid rain on human health
Acid rain has a bad impact on human health directly or
indirectly. Acid rain causes accident directly leading to injuries and death.
Again, due to acid rain, the acidity of pond, lakewater increase. As a result, the pH level of aquatic environment falls below
5.6. Low
pH can cause the death of fish.
People eat these
fish knowingly or unknowingly and hence affected indirectly by acid rain.
Acids of acid rain combine with other chemical in the
air and forms urban smog which can cause lung and heart problems such as,
bronchitis, asthma etc.
Effect of acid rain on agriculture
Sudden acid rains destroyed crops of widespread area.
Acid rain increases the acidity of soil.
As a result, in high acidic soil crops
is not good. Besides, high acidity soil slow the growth of different crops.
Control of acid rain
For control of acid rain, such measures need to be
taken so that SO2 and NOx may mix into the atmosphere as little as
possible.
That is, the contaminant gas those are emitted from the
source of all the gaseous contaminants, before mixing in the air, must be freed
from NOx and SOx by using appropriate technology.
Proper control of fuel, that is, the heat that results
from the contribution of any fuel, most of it has to be used. Less burning offuel will reduce the production of SOx and NOx.
Besides, the fuel with sulfur and nitrogen impurity
should be used as little as possible. Initiatives should be taken to use
alternative fuels for fossil fuels.
That is, CNG and LPG should be used more instead of
sulfur added fuel.
In order to use such technology that must be removed SOx
and NOx gas at the mouth of the emitting contaminants source.
The smoke from the goldsmith's factory contains NO2
that enter into the air.
Before mixing this smoke in the air, it is necessary to
free the NO2 using chemical absorbent method.
- Acid rain definition in environmental chemistry
- What are the sources of acid rain in environment?
- What are the consequences of acid rain in environment?
- What is the contribution of different acids in acid rain?
- What is the pH value of acid rain?












No comments:
Post a Comment