Chemical bonding definition in chemistry
The force of attraction, through which two or more atoms of similar or different elements, are connected to form basic or compound molecule or ion , that force of attraction is called chemical bonding .
The chemical
bond is formed due to electrostatic force of attraction between two or more
atoms with opposite charges or by sharing of electrons among
the different elements.
Chemical bonding examples in chemistry
There are
three types of chemical bonding in chemistry .
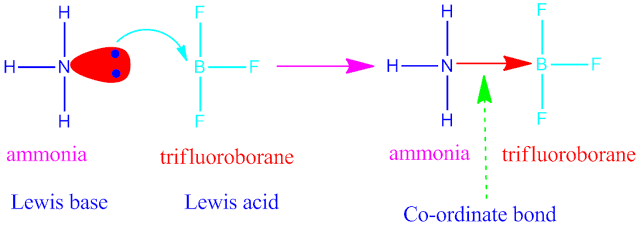
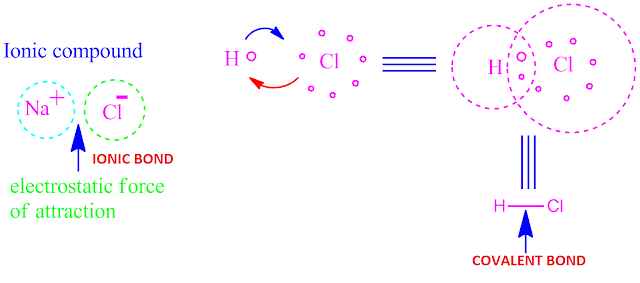
( I ) Electrovalent or ionic bonding ( II )
Covalent bonding ( III ) Co-ordinate bonding or dative bonding .
Besides
this, there are another two type of bonding are also known to us which are
treat as chemical bonding.
They are metallic bonding and hydrogen bonding.
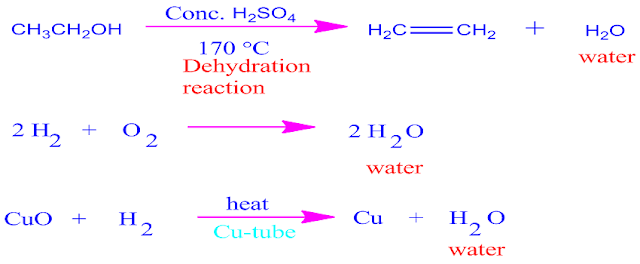
Examples of
the above main three type of chemical bonding
is shown above.
Why elements undergo chemical reaction?
It has been
experimentally found that, the ionization potential of noble gas elements are
very much high but their electron affinity is very much low.
Therefore,
noble gas elements do not takes part in chemical reaction. That is, they are
chemically inactive .
For this
reason, noble gas elements are also called inert gas or zero valent elements .
The
electronic configuration of ‘He’ is 1s2
. But the common electronic configuration of rest of the other inert gas
elements are ns2 np6 .
That is,
except helium , all the noble gas elements contains eight electrons in their
outer most valence shell.
According to Kossel-Lewis theory, most of the
elements have a tendency to maintain eight electrons ( octet rule ) in their
outer most valence shell at the time of chemical reaction , so that they attain
noble gas like electronic configuration.
Because , it
is a more stable electronic configuration. For this purpose, most of the elements
under goes chemical reaction to form more stable basic or compound molecule or
ions.
That is,
they combine to each other to form a union of two or more atoms, through redistribution of their valence
electrons.
Chemical bonding importance in chemistry
There is a
great significant or importance of chemical bonding in chemistry
world. All the compounds ( both organic and inorganic ) are created
with the help of chemical bonding .
Any chemical change or chemical reaction in our
every day chemistry can not happen without formation of chemical
bonding.
Without
chemical bonding any matter ( The earth,
the moon, the stars etc ) in the
world Can not exist .
Because ,
chemical bonding (Electro-valent or
ionic bonding, Covalent bonding ,
Co-ordinate bonding or dative bonding ) connects the atoms or
molecules to each other to form compound as well as matter.
Chemical
bonding helps to joining atoms or molecules together. It is also helps molecules of the same or different substance
to get together through joining to each other .
Solid ,
liquid, or gaseous matter can exist in the nature due to chemical bonding .
Consequently,
chemical bonding is very much important for the existence of matter in the
earth.
Summary
- Chemical bonding definition in chemistry
- Chemical bonding examples in chemistry
- Chemical bonding importance in chemistry
- Why elements undergo chemical reaction ?











No comments:
Post a Comment