What is an inner-metallic complexes in chemistry ?
Inner-metallic complexes are those co-ordination complexes in which the ligand possess both neutral and acidic donor atom or group.
When
a chelating ligand with both neutral as well as acidic group, form one type of chelating complexes ,in which
both the primary and the secondary valency of central metal atom is satisfied by
the ligand simultaneously.
Then
the resulting chelate complexes are called inner-metallic complexes .
For
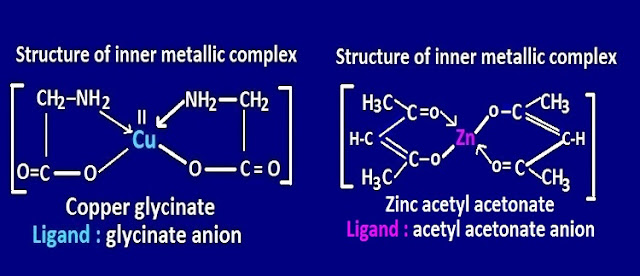
example, copper glycinate , [ Cu ( gly )2
] , zinc acetyl acetonate, [ Zn (acac )2] etc.
The
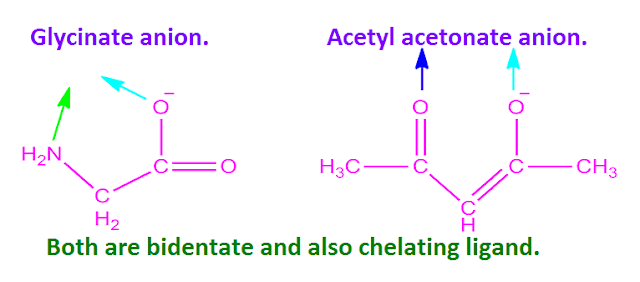
ligands used in the formation of inner-metalliccomplexes are , glycinate anion,
acetyl acetonate anion and other amino acid etc.
All
the Inner-metallic complexes are chelate complexes, but all the chelate
complexes are not Inner-metallic
complexes .
Because, inner-metallic
complexes
are neutral complex compound , but chelate compounds are may be cationic, anionic or neutral type .
Why are inner metallic complexes pH dependent ?
The
ligands which are used in the formation of inner-metallic complexes are
contained both neutral and acidic donor atom or group .
They
satisfied both the primary and the secondary valency of central metal ion
simultaneously.
Hence,
inner-metallic complexes are
generally neutral chelate complex. So, the pH
value of inner-metallic complexes is 7, just middle point on the pH scale.
Summary
What is an inner-metallic complexes in chemistry ?
Examples of inner-metallic complexes.
Why are inner metallic complexes pH dependent ?








No comments:
Post a Comment