What is Ionization energy or ionization enthalpy?
Ionization
energy or first ionization
energy is defined as the minimum amount of energy required to remove the
most loosely bound electron of an isolated neutral gaseous atom, converting
into ion with one unit positive charge.
(Isolated gaseous atom) Ionization energy (Gaseous ion)
Units of ionization enthalpy: Since ionization enthalpy
is related with energy, hence the unit of ionization potential should the same
of energy.
Ionization energy has three types of unit, namely electron volt/atom (eV/atom), kcal/mol, kJ/mol.
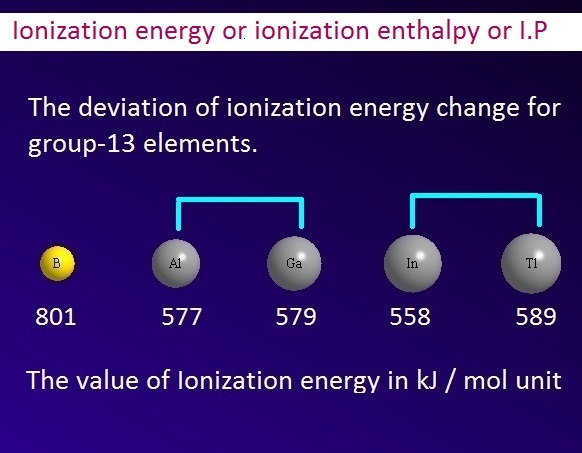
Why does the order of ionization energy value of group-13 elements not regular?
Generally, the order of ionization energy decreases when we move from top to button along a
group.
But, in case of group-13 elements, the order of
ionization enthalpy change is not regular. It has been found that the value of ionization energy from B to Al
decreases.
This is because in this case the combined effect of
increasing the size of the atom and the screening effect exceeds the effective
nuclear charge of the atom.
On the other side, the
value of ionization energy from Al
to Ga slightly (2 kJ/mole) increases.
This is because Ga-atom has 3d-electrons. Now 3d-orbital shows weak shielding effect.
Hence 3d-electrons are unable to shield the outer most valence electrons properly. Consequently, the effective nuclear charge of Ga is slightly higher than Al.
Again, the value of
ionization potential decreases from Ga to In. In case of In, the screening
effect of inner atomic orbital are more effective than effective nuclear
charges.
Hence the effective
nuclear charge for outer most electrons is than expected. So the value of ionization energy of ‘In’ is less than
Ga.
Finally, the value of ionization enthalpy increases from In to Tl. That is, the value of ionization
enthalpy of Tl is higher than In.
In this case, the
effective nuclear charge of Tl atom is more effective than In atom due to weak
shielding effect of 4f and 5d electrons of Tl-atom.
Therefore, the value of ionization energy of Tl-atom is greater
than that of In-atom.
Why is the value of ionization energy of inert gases higher?
The outer electronic configuration of inert gas elements are ns2 np6. That is, each inert gas element occupied eight electrons (octet) in their outer most shell.
Besides, all the inner orbital of inert gas elements are completely filled by electrons. Such type of electronic configuration becomes more stable electronic configuration.
Therefore, a large
amount of energy is required to convert an inert gas into an ion by removing an
electron from the outer most shell. As a result, the value of ionization
energy of inert gas element higher.
Are the values of the first I.E of two isotopes of the same element equal or different?
Ionization
energy of atom or molecule depends
on few factors such as, atomic size, effective nuclear charge, outer electronic
configuration, shielding effect, penetrating power of orbital and half filled
or full filled orbital.
Now, in case of two isotopes
of the same element, the number electrons and their electronic configuration
are equal. Again, their nuclear charge and atomic radius are also identical.
Consequently the values of
the first ionization energy of two
isotopes of the same element should be equal.
- What is Ionization energy or ionization enthalpy or ionization potential?
- Why is the value of ionization energy of inert gases higher?
- Are the values of the first I.E of two isotopes of the same element equal or different?
- Why is the ionization potential of Na+ higher than Ne?
- Why is the ionization enthalpy of Na+ higher than Na?
- Why is the ionization potential of nitrogen higher than oxygen?
- Why is the ionization energy of inert gases higher?
- Why is the ionization potential of phosphorous higher than sulfur?
- Why is the I.P of Cu higher than that of K, even though both have 4s1 electrons in their outer orbital?
Ionization energy definition, ionization
energy of group-13 elements, ionization energy of isotopes, ionization energy
of inert gas elements.









No comments:
Post a Comment