Why is TiCl2 paramagnetic while TiO2 is diamagnetic?
Paramagnetic and
diamagnetic
character of substance depends on the number of unpaired and paired electrons
occupied by that substance.
Any
substances those contain number of unpaired electrons are called paramagnetic
substances. On the other side, if the substance does not contain any odd
electrons, is called diamagnetic substance.
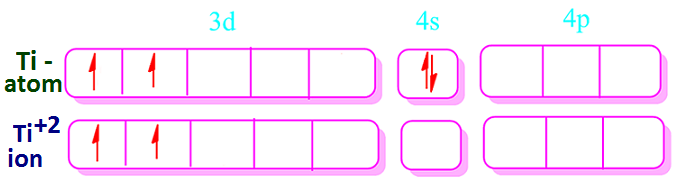
Now, in the case of TiCl2, the oxidation state of Ti atom +2 and the atomic number of Ti atom is 22. Hence, according to Hund’s rule, the outer electronic configuration of Ti+2ion [Ar] 3d2.
The electronic configuration of Ti+2-ion in TiCl2 is shown below.
From
the above electronic configuration it has been found that Ti+2-ion
in TiCl2 has two odd electrons present in its outer 3d-subshell, hence TiCl2 is
paramagnetic
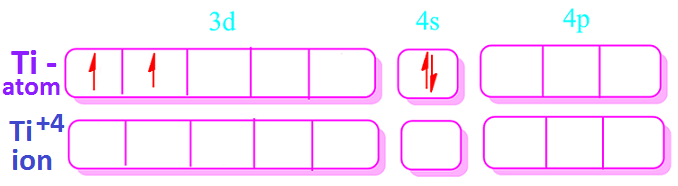
On the other hand Ti-atom in TiO2 shows +4 oxidation states. So, according to Hund’s rule, the outer electronic configuration of Ti+4 ion is [Ar] 3d0. The electronic configuration of Ti+4-ion in TiO2 is shown below.
Evidently,
there is no electron, that is, no unpaired present in Ti+4 ion,
hence
TiO2
is diamagnetic.
Why is [MnCl4] 2– tetrahedral and paramagnetic?
The
Mn (II) ion is 3d5 system.
According to Hund’s rule the outer
electronic configuration of Mn (II) ion
is [Ar] 3d5. From
electronic configuration of Mn (II) ion, it is shown that it has five unpaired
electrons.
Now,
depending upon the hybridization, there are two types of possible structure of Mn (II) complex are formed with co-ordination number 4.
If
the complex involves ‘sp3’ hybridization, it would have
tetrahedral structure. Again, if the complex involves ‘dsp2’ hybridization, it would have square planar
structure.
Consequently,
for the formation of tetrahedral structure through the ‘sp3’ hybridization, the
3d-orbital of Mn- atom remain unaffected.
Therefore,
3d-orbital of Mn (II) ion possessed five unpaired electrons and hence the
concern complex would be paramagnetic.
Now,
in case of [MnCl4] 2– complex ion, Mn (II) ion with co-ordination 4 involves ‘sp3’ hybridization. Hence the geometry of, [MnCl4] 2– complex ion would be tetrahedral.
Under
this condition, the electronic arrangement of
Mn (II) ion is evidently shown that the 3d-orbitals of Mn (II) ion have
five unpaired electrons and hence [MnCl4]
2– complex ion is paramagnetic.
- Why is TiCl2 paramagnetic while TiO2 is diamagnetic?
- Why is [MnCl4] 2– tetrahedral and paramagnetic?
- Why is TiCl2 paramagnetic in nature?
- Why is TiO2 diamagnetic in nature?
TiCl2 paramagnetic while TiO2 diamagnetic, [MnCl4]
2– tetrahedral
and paramagnetic, TiO2
is diamagnetic, TiCl2 paramagnetic,

![Why is [MnCl4] 2– tetrahedral and paramagnetic? Why is [MnCl4] 2– tetrahedral and paramagnetic?](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhydeYdeHqX4yYTelaZqLe3LyaFjcMw2kw1k5jm06Z3eroZ5Dhbd8dbsV3mMO2Bka7Q5tg7ENOt51ODwoeyHw2NSZs3oTrlVpFVV_MN4lwHDDmk6bRNqg16PUM8Xa_j966NgOeLNBCtifc/s16000/Mn+%252B2.png)








No comments:
Post a Comment