What is optical isomerism ?
A compound which contains asymmetric carbon atom that is, a carbon atom linked to four different
groups or atoms, can exists in two isomeric forms which differ in their sign of
rotation, such a compound exhibits optical isomerism.
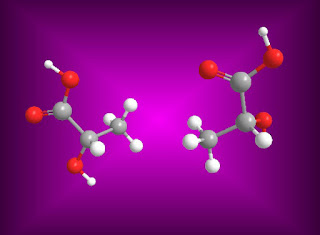
For example, lactic acid .
The 3D isomeric structure of lactic acid are as follows.
What is optical isomers ?
Optical isomers are characterized by
compounds having the same structure but different configuration due to
their molecular asymmetry.
These compounds rotate the plane of polarization of plane
polarized light , either clockwise or anti clockwise.
For example, lactic acid have two optical isomers are as follows.
What is condition of optical activity ?
The necessary and sufficient conditions for a molecule to
exhibit optical activity is,
( I) the molecule will not be super imposable on its mirror
image and
(II) the molecule possess
none of the symmetry elements
such as plane of symmetry, centre of symmetry, or alternating axis of
symmetry.
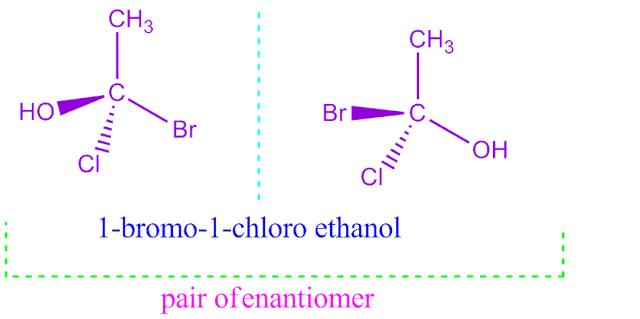
What is enantiomers ?
Optical isomers are mirror image to each other but not superimposable,are called enantiomers.
For example, 1-bromo-1-chloro ethanol have two enantiomeric forms are shown below.
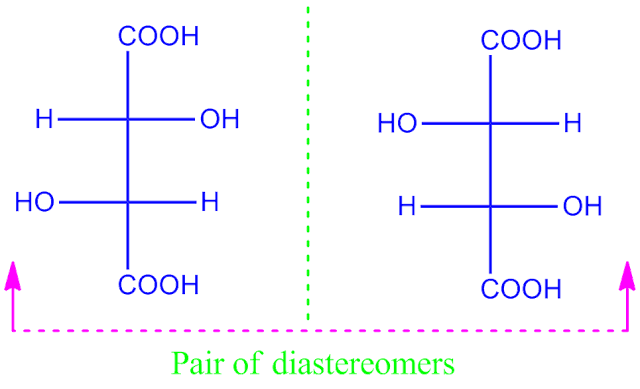
What is diastereomers ?
Optical isomers are not mirrorimage to each other and not superimposable are called diastereomers.
For example, tartaric acid have a pair of diastereomers.
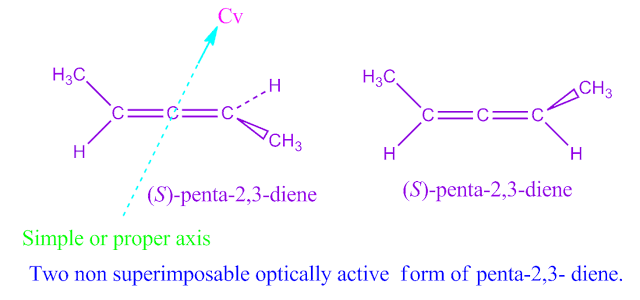
What is dissymmetric molecule ?
If a molecule possess a simple or proper axis of symmetry but does not possess plane of symmetry, center of symmetry or alternating axis of symmetry, such a molecule is termed as dissymmetric molecule and they are also optically active.
For example, 1,3 dimethyl allene or penta-2,3-diene.
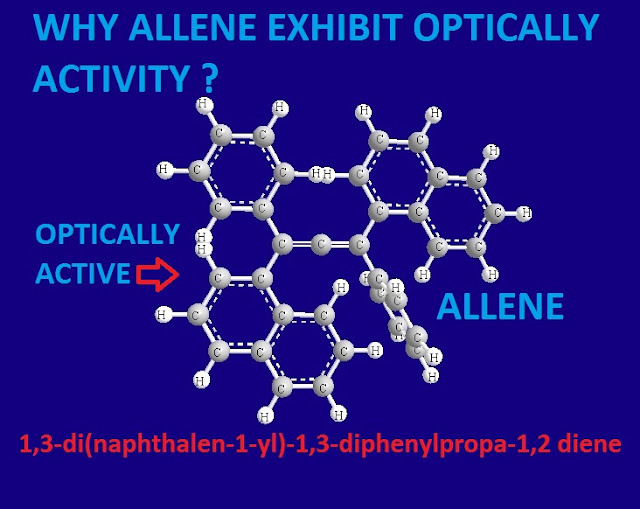
Why allene exhibit optically activity ?
There are few compounds have no asymmetric carbon atom yet they exhibit optical isomerism. Because, as a whole the molecule becomes asymmetric due to restricted rotation and absence of any elements of symmetry.
Summary:
optical isomerism, optical isomers.
Enatiomers, diastereomers .
Dissymmetric molecule and optical activity of allene.
Practice problem:
Why spirans exhibit optically activity ?
What is the cause of optically activity of biphenyl ?

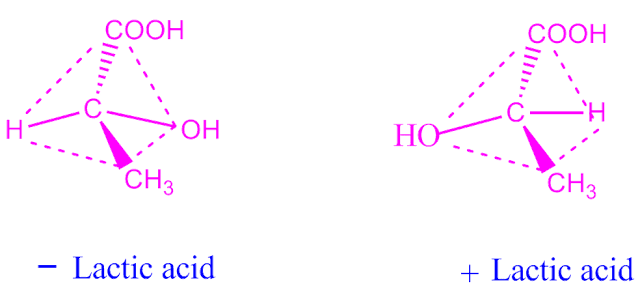








you are clear my mind actually after reading your article i got clear my complete doubt. thanks for such easy understanding post. Sharing on What is the difference between structural and conformational isomers? for future aspect at here http:// electrotopic. com/what-is-the-difference-between-structural-and-conformational-isomers/
ReplyDeleteyou are clear my mind actually after reading your article i got clear my complete doubt. thanks for such easy understanding post. Sharing on What is the difference between structural and conformational isomers? for future aspect at here http://electrotopic.com/what-is-the-difference-between-structural-and-conformational-isomers/
ReplyDeleteVery nice all my
ReplyDeletedoubt are clear
Thanks
DeleteThanks for your good comment.
Delete