What is inductive effect ?
When a hetero atom of different electronegativities is
attached to the ending carbon of a carbon chain , then a permanent displacement
of covalently bonded electrons
occurs toward the more
electronegative atom, which create a permanent polarization in molecule.
So,inductive effect
may be defined as the permanent but partial displacement of electron
along the bond in a molecule actually toward the more electronegative atom due
to electronegative difference of the atom forming the covalent bond.
n-propyl chloride
This inductive effect is sometimes reffered to as a
transmission effect, since it takes place by a displacement of the intervening
electrons in the molecule.
For example, when Cl –atom is attached to the ending carbon of a carbon chain , the displacement of electron of C- Cl bond occurs toward the more electronegative chlorine atom .
Again, if Li atom is attached to the ending carbon of a carbon chain , the displacement of electron of C- Li bond occurs toward the carbon atom .
In both cases, a permanent polarity arises in the molecules are as follows,
Influence of Inductive effect on physical and chemical properties of a molecule.
As a result of inductive effect there are many physical and
chemical properties of organic molecule
changes. For example, strength of acid and base , dipole moment etc changes due
to inductive effect.
What is field effect ?
There is another effect almost similar to inductive effect
which operate either through the space surrounding the molecule or in solution
through solvent molecule ,is called field effect.
However, in many cases field effect can not be distinguish
from inductive effect.
Why dipole moment of cis-2-butene is greater than trans-2-butene?
Dipole moment of cis-2-butene is greater than trans-2-butene
due to inductive effect of methyl group which acts in the same direction for
cis-2-butene but for trans it acts in opposite direction.
Why formic acid is more stronger than acetic acid ?
The strength of acid depends on the stability of anion of
that acid. On ionization, formic acid gives formate anion and acetic acid gives
acetate anion. Both the formate and acetate anion have two equivalent resonating
structure .
But in case of acetic acid , methyl group has +I effect . As a result , the density of electron on oxygen atom increases. Hence, the stability of acetate anion is less than formate anion.
But in case of acetic acid , methyl group has +I effect . As a result , the density of electron on oxygen atom increases. Hence, the stability of acetate anion is less than formate anion.
Consequently, the formic acid is more stronger than acetic acid.
Why chloro acetic acid is more stronger than acetic acid?
The strength of acid depends on the stability of anion of
that acid. On ionization, acetic acid
gives acetate anion and chloro acetic acid gives chloro
acetate anion.
Both the acetate and chloro acetate anion have two equivalent resonating structure . But in case of chloro acetic acid , chlorine atom has -I effect .
As a result , the density of electron on oxygen atom decreases. Hence, the stability of chloro acetate anion is greater than acetate anion.
Both the acetate and chloro acetate anion have two equivalent resonating structure . But in case of chloro acetic acid , chlorine atom has -I effect .
As a result , the density of electron on oxygen atom decreases. Hence, the stability of chloro acetate anion is greater than acetate anion.
Consequently, the chloro acetic acid is more stronger than acetic acid.
Why methyl amine is stronger base than ammonia ?
The strength of base depends on the electron donating power
of the concerned base. In case of methyl
amine, the density of electron on N-atom increases due to the +I effect of
methyl group and a repulsive force arises among the electronic charge.
As a result of this, the tendency for donating of electron of methyl amine is increases. Hence, basicity of methyl amine increases.
As a result of this, the tendency for donating of electron of methyl amine is increases. Hence, basicity of methyl amine increases.
For the above reason, methyl amine is stronger base than ammonia.
Compare the basicity of primary , secondary and tertiary amine in aprotic solvent.
The strength of basicity of primary, secondary and tertiary
amine depends on their electron donating power. Primary
amine,secondary amine and tertiary amine
contain one ,two and three alkyl group respectively.
Now, alkyl groups have +I effect . So the density of electron on N-atom is highest for tertiary amine and lowest for primary amine and hence the repulsive force among the electronic charge is the same order.
Therefore, the tendency for donating of electron of tertiary amine is greater than the primary and secondary amine.
Now, alkyl groups have +I effect . So the density of electron on N-atom is highest for tertiary amine and lowest for primary amine and hence the repulsive force among the electronic charge is the same order.
Therefore, the tendency for donating of electron of tertiary amine is greater than the primary and secondary amine.
Consequently , in aprotic solvent the basicity order of
primary , secondary and tertiary amine are as follows,
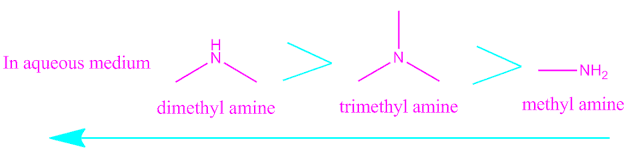
Compare the basicity of primary , secondary and tertiary amine in aqueous medium.
The basicity of primary , secondary and tertiary amine in aqueous solution depends on the stability
of their respective the conjugate acid .
Now, the stability of conjugate acid of different amine depends on two factors , one is inductive effect of alkyl group and the another is hydrogen bonding.
Considering this two factor ,it has been experimentally found that the conjugate acid of secondary amine is more stable than the other two.
Now, the stability of conjugate acid of different amine depends on two factors , one is inductive effect of alkyl group and the another is hydrogen bonding.
Considering this two factor ,it has been experimentally found that the conjugate acid of secondary amine is more stable than the other two.
Hence, in aqueous solution the secondary amine behave as a stronger base
than primary and tertiary.
Depending on stability of conjugate acid , the basicity
order of primary , secondary and
tertiary amine in aqueous medium are as
follows,
Practice problem:
Why chloramine is weak base than ammonia ?
What is inductive effect ? give example .
What is field effect ?
















you are clear my mind actually after reading your article i got clear my complete doubt. thanks for such easy understanding post. Sharing on What is the difference between cis and trans isomers? for future aspect at here http://electrotopic.com/what-is-the-difference-between-cis-and-trans-isomers/
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDelete