Chelate complex definition in co-ordination chemistry.
When a bidentate or poly dentate ligand is attached to the central metal atom or ion through two or more donor atoms, resulting in the formation of a ring structure complex in the co-ordination sphere ,then the resulting complex is known as chelating complex .
Chelate complex examples in co-ordination chemistry.
There are
few well known chelating complex in co-ordination chemistry. Such as Ni( DMG )2 , [ Fe ( C2O4
)3 ]3– etc .
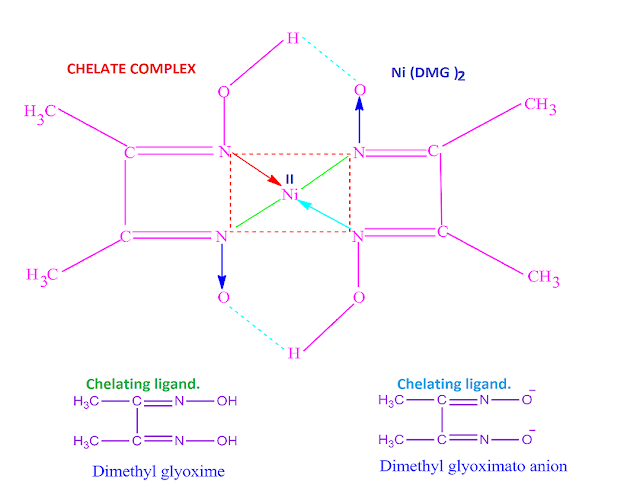
Dimethyl glyoxime (dmg ), a chelating ligand which
forms a neutral chelate complex with nickel metal .
Besides,
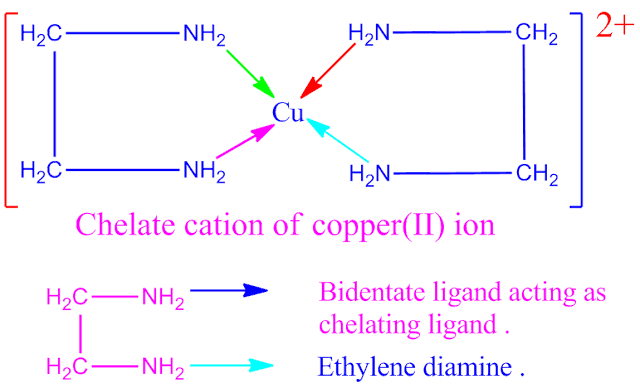
ethylene diamine , a bidentate ligand which is also a chelating ligand . It
forms chelate cation with Cu 2+ ion .
Similarly,
oxalate anion acts as a chelating ligand in the formation of a chelate anion, [ Fe ( C2O4 )3 ]3–.
What is meant by chelating ligand’s?
When a bidentate or poly dentate ligand is
attached to the central metal atom or ion through two or more donor atoms
forming a ring structure in the co-ordination sphere, then these type of
ligand’s are called chelating ligand’s .
Such as glycinate anion ( gly–
) , oxalate anion ( Ox 2– ) , dimethyl glyoximato anion ( dmg–
) , acetyl acetonate anion (acac– ) , ethylene diamine (en
) , 2,2’dipyridyl ( dipy ) , ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) etc .
Why does ethylene diamine is called chelating ligand?
Ethylene diamine , a bidentate ligand . When it co-ordinates with Cu 2+ ion through both the nitrogen atoms , it forms a ring structure complex cation in co-ordination sphere . Hence ethylene diamine is called chelating ligand.
Why does oxalate anion is called chelating ligand ?
Oxalate
anion, a bidentate ligand. When it co-ordinates with Fe 3+ ion
through both the oxygen atoms, it forms a ring structure complex anion in co-ordination sphere, [ Fe ( C2O4 )3 ]3–. Hence oxalate anion is called
chelating ligand.
Significance of chelate formation .
( I ) The quantitative estimation and identification of
some metal ions [ Cu 2+, Ni 2+, Mg 2+ , Al 3+ etc ] are done by the formation of
chelate complexes.
( II ) The
permanent hardness of water can be removed by the formation of chelate
complexes. Such as Mg 2+ ,
Ca 2+ etc ions in hard water can be removed through the
formation of Ca – EDTA or Mg – EDTA chelate complex.
( III ) Separation of lanthanides elements from actinides
elements is possible through the formation of chelate complex .
( IV ) Metal
ion toxicity increases due to incorporation of different metal ion [Hg 2+,Pb 2+ , Cd 2+ etc ] in our human body. These toxic metal ions are
eliminated from our body through the formation of chelate complex .
In this
purpose , EDTA –chelating ligand is used to remove the above said ions.
Besides, for Pb 2+ ion toxicity, Na2[Ca ( EDTA )] agent is used to remove Pb 2+ ion from human body .
( V ) Chelating
complex formation process is also used to preservative of different food and
solvent extraction .
What is π-acid or π-acceptor ligand’s ?
The π-acceptor ligand’s are those which possess vacant
p-orbitals in addition to the lone pair of electrons .
These ligands donate
their lone pair to the metal to form a normal sigma( σ ) bond with the latter.
In addition
to it , the vacant orbitals accept electrons from the filled metal orbitals to
form a type of π-bond which suppliments the sigma
bond .
These ligand’s are thus called π-acid ligand’s or π-acceptor ligand’s.The π-acid ligand’s are also called π-bonding ligand’s .
Examples of π-acid ligand’s.
The common
examples of π-acid ligand’s are CO , R–NC , NO , PR3 etc .
Chelate complex definition in co-ordination chemistry .
Chelate complex examples
in co-ordination chemistry .
What is meant by chelating
ligand’s ?
Why does ethylene diamine
is called chelating ligand ?
Why does oxalate anion is
called chelating ligand ?
Significance of chelate
formation .
What is π-acid
or π-acceptor ligand’s ?










No comments:
Post a Comment