What are transition metals?
Elements
that have a partially filled d-sub-shell in the atomic
state or permanent oxidation state are called transition metals. Generally, d-block elements are known as transition metal elements.
The periodic table contains the transition metals between the s-block and p-block elements. The common electronic configuration of outer most valence shell of transition metal elements are (n-d)1-10 ns1-2 .
All
the transition metal elements are
metal. But they are less electropositive than s-block elements and more
electropositive than p-block elements.
The
transition metal elements consists
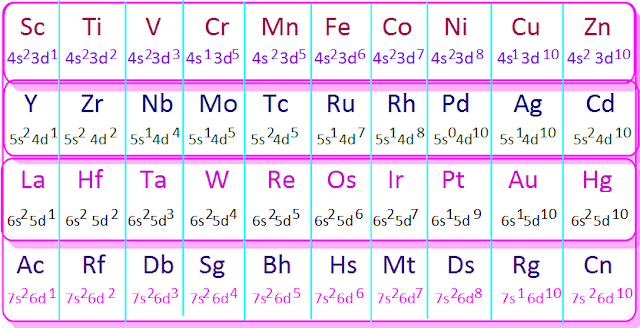
of four rows called first transition or 3d-series, second transition or
4d-series, third transition or 5d-series and forth transition or 6d-series.
The
elements from scandium to zinc constitute the first transition or 3d-series.
The ten elements from yttrium to cadmium constitute the second transition or
4d-series.
Again
from La to Hg these ten elements form the third transition 5d-series and from
actinium (Ac) to Copernicium (Cn) these ten elements
form the forth transition
or 6d-series.
General properties of transition metal elements:
Transition metal elements are metallic
elements with high melting point and boiling point (exception Hg). They are good conductors of heat and
electricity.
The value of the ionic potential of the transition metal elements is higher than that of the s-block element but lower than that of the p-block. Their electro-positivity is less than s-block element but more than p-block element.
The transition metal elements show multiple oxidation number and
valence. Because of their atoms have d-orbitals. During a chemical reaction,
the s-electrons and one or more d-electrons of transition metal take part in the reaction.
Most of the transition metal form colored
compounds. As the oxidation state changes, so does the color. Most transition metal elements form colored
complex compounds due to their small size and high nuclear charge.
Most of the transition metal elements contain one
or more odd d-electrons in their atomic or ionic state. This is why they show
paramagnetic properties.
Most of the transition elements are used as catalysts in chemical reactions in the free or added state. They also have a tendency to form alloys.
Why are transition metal called transition metals?
Transition metals are called transition metals due to two causes.
Firstly, elements that have a partially filled d-sub-shell
in the neutral state or permanent oxidation state are called transition metal elements.
Since
transition metal elements have a
partially filled d-sub-shell in their outer most shell hence they are
called transition metals.
On
the other hand, transition metal elements
are present in between s-block and p-block elements in the periodic table.
Their ionization energy is higher than s-block elements but lesser than p-block
elements.
Hence
transition metal elements are less
metallic than s-block elements and more metallic than p-block elements.
That
is, the transition metal elements
act as a bridge between ‘s’ and ‘p’ blocks elements and show a transition in
the properties from the metals to the non-metals, thus they are also called transition metals.
Why are all transition element d-block elements but all d-block elements not transition elements?
The element in which the
electrons in the outermost shell enter the d-sub-shell, are called d-block
elements.
On the other hand, metal elements that have partially filled d-orbitals are
called transition metals.
That
is, in case of d-block elements, they can occupy partially filled d-orbitals or
completely full filled d-orbitals in the atomic state or in the permanent
oxidation state.
But
transition metal elements must
occupy partially filled d-orbitals in the atomic state or in the permanent
oxidation state.
For
example, Zn, Cd, Hg occupied completely filled d-orbitals either in their
atomic state or in their permanent oxidation state. Hence Zn, Cd and Hg are
d-block elements not transition metal elements.
For this reason it is said
that,
all transition metal elements are
d-block elements but all d-block elements are not transition metal elements.
Why Zn, Cd, Hg are not called transition elements?
According to definition, transition elements are those that have a
partially full d-sub-shell in the atomic state or permanent oxidation
state.
But in case of Zn, Cd, Hg,
the d-sub-shell is completely filled in atomic state or in permanent oxidation
state. For this reason, Zn, Cd and Hg are not called transition elements.
- What are transition metals?
- Why Zn, Cd, Hg are not called transition metal elements?
- Why are transition metal called transition metals?
- Why are all transition element d-block elements but all d-block elements not transition elements?
Transition
metals, transition elements, transition metals properties, Zn,
Cd, and Hg are not called transition elements,


No comments:
Post a Comment