What is nitric acid (HNO3) in chemistry?
There are seven oxo acids of nitrogen are known. Nitric acid is one of them with molecular formula HNO3. Nitric acid is a highly corrosive mineral acid.
Most
of the metals and non metals are soluble in nitric acid. For this reason, nitric
acid is also known as aqua fortis, its mean ‘strong water’.
Pure nitric acid is a colorless liquid at room
temperature, but older sample of nitric acid may be yellow or reddish brown
color. It is suffocating and also acrid smelling acid.
It is smoked in humid air. The melting point of pure HNO3 is 231K and the boiling point of pure nitric acid is 355.6K.
When
concentrated nitric acid comes in contact with our skin, it form painful sores
on the skin and the skin turns yellow.
What is nitric acid formula and structure?
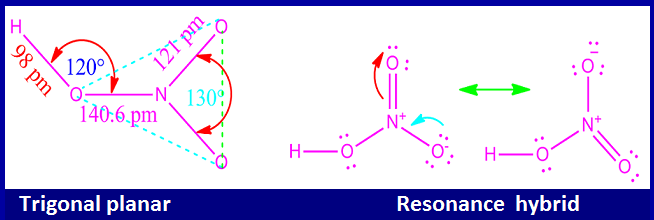
The central N-atom of HNO3 molecule is sp2 hybridized.
Therefore, the geometry of nitric acid is trigonal planar.
Actually, nitric acid has two different resonatingstructures. These two resonance hybrid of HNO3 are shown below.
What is fuming or red fuming nitric acid?
Pure nitric acid is a colorless liquid. But when nitric
acid is left in sunlight for a long time, nitric acid decomposes to produce NO2
and O2.
In
this condition, when the bottle of nitric acid is opened, a reddish brown color
of NO2 gas is emitted. This reddish brown
nitric acid with NO2 is called fuming nitric acid.
Again, when concentrated nitric acid is distilled with a
small amount of As2O3 or starch, the obtainable nitric acid is called fuming
nitric acid.
Now, depending
on the amount of NO2 present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as
red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid
at concentrations above 95%.
How to prepare nitric acid?
There
are two methods for preparation of nitric acid. One is laboratory preparation
method and the other is industrial preparation method.
Laboratory
preparation:
In
laboratory, nitric acid is prepared by heating of mixture of KNO3 or NaNO3 and
concentrated sulfuric acid at 200ᵒC.
The
reaction takes place in two steps. In first step, KHSO4 and HNO3 is obtained by
the reaction of KNO3 and concentrated sulfuric acid at 200ᵒC-230ᵒC.
In
the second step, the producing KHSO4 reacts with unaltered KNO3 produces K2SO4
and HNO3. The reaction occurs at 800ᵒC.
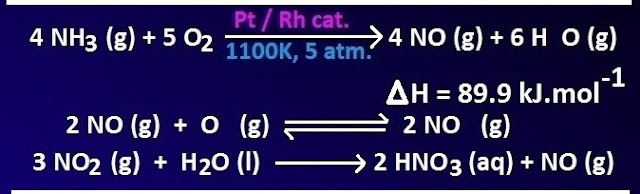
Industrial preparation of nitric acid (Ostwald method):
Nitric
acid is prepared industrially by Ostwald method. This method consists of three
steps.
In first step, ammonia is oxidized to NO by air oxygen in presence of platinum or Pt-Rh catalyst. The reaction takes place at 1100K temperature under 5 atmosphere pressures. In the second step, the producing NO is further oxidized by air to NO2.
Finally
NO2 is absorbed by water to produce nitric acid and NO. It is dilute nitric
acid. 68% concentrated nitric acid is obtained by distillation of this dilute
nitric acid.
Then,
on dehydrating this nitric acid by sulfuric acid we can get 98% concentrated
HNO3.
What is concentrated nitric acid?
The nitric acid that is produced in commercially method is dilute nitric acid. Now, on distillation of this dilute nitric acid, 68% concentrated nitric acid solution is obtained.
It is a constant boiling azeotropic mixture. Two
solid hydrates of nitric acid are known: the mono hydrate (HNO3.H2O) and tri
hydrate (HNO3.3H2O).
This nitric acid is known as concentrated nitric
acid. The strength of this nitric acid solution is about 16(N).
Nitric acid pH calculation
It is soluble in water in any proportion. When the aqueous
solution of nitric acid is evaporated at 120.5ᵒC at one atmosphere, it gives 68%
HNO3 solution. It is an example of azeotropic mixture.
Distillation
of 68% concentrated HNO3 with concentrated H2SO4 yields 98% concentrated HNO3.
Now, it has been experimentally found that the strength of
concentrated HNO3 is approximately 16(N).
Since nitric acid is a strong monobasic acid, it
dissociates completely in aqueous solution.
Hence the concentration of H+ ion is equal to the
concentration of HNO3. That is, the concentration of H+ ion is 16(N).
Therefore, pH= - log [H+] = - log16 = - 1.20.
What are uses of nitric acid?
Nitric
acid is a very strong oxidizing agent. It is used as an oxidizing agent in
organic as well as in inorganic chemistry.
Nitric
acid is used to prepare ammonium nitrate, basic calcium nitrate etc fertilizer.
Again, ammonium nitrate is used to prepare explosive matter.
Nitric
acid is also used to prepare different explosive such as, nitro glycerine, RDX,
nitro cellulose, tri nitro toluene, picric acid etc.
Cyclo
hexanone, adipic acid etc raw materials of nylone are made by using nitric
acid. Besides, terephthalic acid which is a raw material of terylene, is also
prepared by nitric acid.
Nitric
acid is used as aqua regia (3 portion of HCl + 1 portion of HNO3) to purify
gold and platinum.
It is used in stainless steel pickling and cleaning, as an
oxidizer in rocket fuel, in the preparation of various nitrate compounds, and
as an important reagent in the laboratory.
What is nitric acid hazard?
Nitric
acid is a corrosive acid as well as a powerful oxidizing agent. The major
hazard posed by its chemical burns.
Exposure
to nitric acid causes painful sores on the skin and yellowing of the skin. The body's protein
substance reacts with concentrated nitric acid to form a yellow compound called
xanthoprotein.
Again,
fish die due to acid rain or mixing of nitric acid in water from factories. Because
of the body of the fish is made of protein.
- What is nitric acid (HNO3) in chemistry?
- What is nitric acid formula and structure?
- What is fuming or red fuming nitric acid?
- How to prepare nitric acid?
- What is concentrated nitric acid?
- Nitric acid pH calculation
- What are uses of nitric acid?
- What is nitric acid hazard?
Nitric
acid, HNO3, nitric acid formula, uses of nitric acid, fuming nitric acid,
nitric acid hazards, concentrated nitric acid, nitric acid charge, nitric acid
pH, conc. HNO3,










No comments:
Post a Comment