Hydrogen fluoride details in halogen chemistry
Hydrogen fluoride is a chemical compound of hydrogen and fluorine with molecular formula, HF. It is a polar covalent hydride. Hydrogen fluoride is a colorless, odorless, highly poisonous gas.
Hydrogen
fluoride is a mono basic weak acid
when dissolved in water. The pKa value of HF acid is 3.4.
The
molecular weight of hydrogen fluoride is 20.01. The melting and boiling point of hydrogen fluoride are, –83.6 ᵒC and 19.5 ᵒC respectively.
Although,
hydrogen fluoride is a covalent hydride yet it has more ionic character, due smaller size and high electronegativityof fluorine atom.
Due
to this ionic character of HF
molecule, the bond dissociation energy of HF
is higher than that of other halogen acids. The dipole moment of H–F
molecule is 1.86 D.
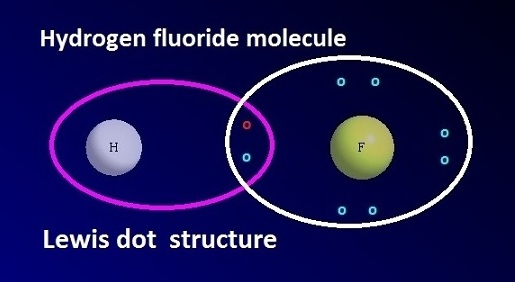
Hydrogen fluoride formula and Lewis dot structure
The
chemical formula of hydrogen fluoride is HF. Hydrogen fluoride molecules are associated both in aqueous solution and in solid state through hydrogen bonding. The
Lewis dot structure of hydrogen
fluoride is shown below.
Hydrogen fluoride preparation
There
are different methods for the
preparation of hydrogen fluoride
gas.
For
example, reaction of hydrogen with very reactive fluorine element produce
hydrogen fluoride.
Since fluorine is very reactive, hence it
reacts with hydrogen explosively, even in the dark, forming hydrogen
fluoride.
Hydrogen
fluoride
is also prepared industrially and in
the laboratory by the
reaction of calcium
fluoride or sodium chloride individually with concentrated sulfuric acid.
Hydrogen fluoride properties details in chemistry
Hydrogen fluoride hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen
fluoride is liquid at room temperature. Because, being polar hydrogen fluoride
molecules are associated through inter molecular hydrogen bonding.
In
solid state, hydrogen fluoride forms a zig-zag type of inter molecular hydrogen
bonding in which the bond angle of H – F ……H is 116ᵒ.
Although,
the chain is shorter and it consist of five or six HF molecule.
Hydrogen fluoride is liquid at room temperature
Hydrogen fluoride is liquid at room temperature
due to formation of inter molecular hydrogen bonding. HF
molecules get associated through the formation of inter molecular hydrogen bonding.
Hydrogen fluoride melting point and boiling point
Hydrogen fluoride molecules get associated
through the formation of inter molecular hydrogen bonding and hence HF isliquid at room temperature.
But the other halogen acids do not form hydrogen bonding.Now, some amount of heat energy is required to break this hydrogen bonding in HF molecule.
Consequently, the boiling point and melting point of hydrogen fluoride is higher than that of other halogen acids [ HCl, HBr, HI etc ].
Although,
the melting point of hydrogen fluoride molecule is than HI .Because of the
higher molecular weight and greater inter-molecular Vander waal’s forces of HI molecule.
Dipole moment of hydrogen fluoride
Fluorine
is more electronegative than other halogens. Hence H–F bond is more polar than
H–Cl, H–Br and H–I bond.
Hence
H–F molecule has a greater dipole moment value than other halogen acid. The
calculated dipole moment value of hydrogen fluoride is 1.86 D.
Hydrogen fluoride bond dissociation energy
The
bond dissociation energy of H–F bond is higher than H–Cl, H–Br and H–I bond.
Hence, H – F is more stable compound than, HCl, HBr and HI molecules.
Since
the bond dissociation energy of H–F bond is so high than other halogen acid,
hence HF acid has a weak reducing properties than other halogen acid.
Hydrogen fluoride bond length and bond angle
Hydrogen
fluoride is a diatomic molecule with molecular structure HF in gaseous state
and H2F2 in aqueous solution.The
bond length of hydrogen fluoride molecule is 98.8 Pico meter.
In
solid state, hydrogen fluoride forms a zig-zag type of inter molecular hydrogen
bonding in which the bond angle of H – F ……H is 116ᵒ.
Hydrogen fluoride pH calculation.
Hydrogen
fluoride is highly soluble in water. The concentrated aqueous solution of
hydrogen fluoride is known as hydrofluoric acid.
The
density of hydrofluoric acid solution is 1.15 g/ml or 1150 g/litre. Now,the
molecular weight of HF molecule is 20.01. But
in aqueous solution, HF forms dimer structure due to abnormal association.
So,
molecular weight of H2F2 dimer is 40.02 instead of 20.01.
So, the molar strength of HF weak acid is 28.8 mole/liter or 28.8 (N).
Since
HF is a weak acid and the pH of HF can’t be calculated directly. The pH of weak HF acid is calculated by determining the
dissociation constant(Ka) of weak HF acid.
Now,
the experimental Ka value of HF acid is 3.5 x 10 –4. So,
pKa value of HF is 3.4. Therefore,
the pH of weak HF acid is,
Hydrogen fluoride is a weak acid.
Hydrogen
fluoride is highly soluble in water. The concentrated aqueous solution of
hydrogen fluoride is known as hydrofluoric acid.
However,
HF is a weak acid with compare to the other halogen acid, like HCl, HBr, HI
etc.
Because,
the bond dissociation energy of H – F bond is higher than H–Cl, H–Br and H–I
bond. Hence, the degree of ionization of HF in aqueous solution is less than
other halogen acids.
Besides,
F–ion in aqueous solution gets associated with the non ionized HF molecule and
form HF2–ion. As
a result, HF acid produces lesser number of H+ ion in aqueous solution.
Hence
hydrogen fluoride acid strength is less than H–Cl, H–Br and H–I acid. This
fact has been proved by the measurement of their pKa value. The
pKa value of HF, HCl, HBr and HI acids
are , +3.4 , –7 , –9 , –11 respectively.
The
lesser the pKa value, higher is the acid strength.That
is, HF is a weakest acid and HI is a strongest acid among halogen acids.
Hydrogen fluoride uses in organic and inorganic chemistry
There are many uses of hydrogen fluoride in organic and inorganic chemistry.
Hydrogen
fluoride is used to make refrigerants, herbicides, pharmaceuticals,
gasoline,
stainless steel kitchen products, aluminum, plastics, electrical components and
incandescent light bulbs etc.
60%
of the hydrogen fluoride used in manufacturing of refrigerants, used in
refrigeration, freezer and air conditioning systems.
It also is used in
manufacturing silicon semiconductor chips. In
general, anhydrous HF molecule is
common industrially than its aqueous form, hydrofluoric acid.
Hydrogen fluoride is used as a solvent.
Hydrogen
fluoride is one of the most important water like solvent. Since it is liquid in
at temperatures below 19.5 C upto –89.4
C .
The dipole moment of HF [1.86D] and dielectric constant [83.6] are also
quite close to those of water. Because
of its high dielectric constant, it
serves as an excellent ionizing solvent.
Although, the use of HF is limited because, it
is highly poisonous . HF causes the solubility, conductivity and solubility of
compounds.
Organic compounds such as benzene, ethanol,
alkanes get protonated when dissolved in HF. Because
of the formation of ions, the above said organic compounds give conducting
solution in HF.
The
aromatic hydrocarbons give colored solution in HF and their solubilities can be
increased further by adding fluoride acceptors as BF3 and SbF5.
HF is used to prepare fluorocarbon from chloro carbon.
Hydrogen
fluoride is used to prepare fluorocarbons from chloro-carbons. An
important reaction of hydrogen fluoride to form chloro carbon is the production tetra fluoro ethylene or Teflon .
Again,
HF reacts with acetylene in the presence of ‘Hg’ catalyst and form
1,1-difluoroethane.
HF is used to prepare fluorine and metal fluorides.
HF
is the pioneer to elemental fluorine, by electrolysis of a solution of HF and
anhydrous KHF2. In
this method a large amount of F2 is prepared per every year.
HF
forms few addition compound with metal fluorides, such as, with KF, it form KHF2, KF.2HF, KF.3HF and NH4F.HF etc.
HF is used as catalyst.
HF
is used as a catalyst in alkylation process in refineries. It is used in the
majority of the installed linear alkyl benzene production facilities.
Why is HF less acidic than HI ?
Hydrogen fluoride is highly soluble in water. The concentrated aqueous solution of hydrogen fluoride is known as hydrofluoric acid.
Now,
fluorine is more electronegative than iodine. Hence HF bond is more polar than
HI bond.
So,
HF should be more acidic than HI. But actual order is reversed.That
is, HF is a weak acid with compare to HI acid.
Because,
the bond length of HF is shorter than HI but the bond dissociation energy of H
– F bond is higher than H–I bond. Hence,
the degree of ionization of HF in aqueous solution is less than HI acid.
Again,
F–ion in aqueous solution gets associated with the non ionized HF molecule and
form HF2– ion. As
a result, HF acid produces lesser number of H+ ion in aqueous solution.
Hence
HF acid strength is less than H–I acid.This fact has been proved by the
measurement of their pKa value.
The
pKa value of HF and HI acids are, +3.4 ,–11 respectively. The
lesser the pKa value , higher is the acid strength. Besides,
the heat of ionization of HI is –57 while that of HF is –12.
The
larger the negative value of heat of ionization, the greater is the feasibility
of the ionization reaction and hence the greater is the acidic strength of HI
acid.
Consequently,
HF is a weakest acid and HI is a strongest acid among halogen acids.
- What is hydrogen fluoride in chemistry?
- Properties of hydrogen fluoride.
- How to calculate the pH of HF acid ?
- Is hydrogen fluoride a strong acid ?
- Why is HF a weak acid ?
- Why is HF less acidic than HI ?
- What are uses of HF acid ?
hydrogen
fluoride, HF, hydrogen fluoride properties, hydrogen fluoride uses, hydrogen fluoride
pH calculation,









No comments:
Post a Comment