What is chelating effect in co-ordination chemistry ?
Chelating effect is related to the stability of complex in co-ordination chemistry.
It has been
experimentally found that chelate complex which made by chelating ligand, are
more stable than complex compound made by mono dentate ligand.
This
contribution of chelating ligand to enhance the stability of chelating complex,
is known as chelating effect.
For example,
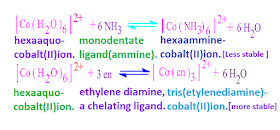
let us consider the formation of complexes from the hydrated cobalt ion ,[ Co ( H2O )6 ] 2+
with ammine [ mono dentate ligand] and ethylene diamine [a bidentate and
also chelating ligand ] ligands in aqueous medium is as follows,
From the above two equation it is seen that , in case of second equation, the number of particle increase after reaction. Hence entropy increases.
That is, in
second cases, free energy of the system, decreases [ ΔGᵒ = ΔHᵒ –TΔSᵒ ].
Consequently,
it is clear that chelate complex which made by chelating ligand, are more
stable than complex compound made by mono dentate ligand.
What is EAN rule in co-ordination chemistry ?
Sidgwick introduces a rules, depending on the
effective atomic number of the central
metal atom to explain the stability of
co-ordination complexes, are known as effective atomic number rules or EAN
rule.
Sidgwick stated that, in co-ordination
complex, the value of effective atomic number is equal to the atomic number in
the next noble gas element.
In the
formation of a complex, each ligand is considered to be donating one electron
pair to the central metal ion.
The total
number of electrons which the central metal ion appears to possess in the
complex including those gained by it in bonding, is called ( EAN ) or effective
atomic number of the central metal ion .
It has been
found that in many cases ligands are added until the central metal ion gets the
same number of electrons as are present in the next noble gas.
Accordingly,
the effective atomic number in a complex should be equal to 36(Kr) ,54(Xe) or 86( Rn ).
The
mathematical expression of effectiveatomic number ( EAN ) is ,
EAN = [ atomic number of metal atom –
oxidation number of metal atom ] + 2 x number of ligands.
Calculation
of effective atomic number( EAN ) of some metal atoms are given below.
Application of EAN rule in co-ordination chemistry .
The number
of ligands that attached to the central metal ion in co-ordination complex, can
be calculated with the help of this theory.
For example,
calculation of ligand numbers in nickel carbonyl compound .
Atomic
number of nickel is 28 . The atomic number of the next inert gas is 36( Kr ).
The number
of electrons are contributed by the ligand due to formation of co-ordinate with
the central metal atom is ( 36 – 28 ) = 8 .
Now, each
ligand contributes two electrons in co-ordinate bond formation .
Hence, the
number of carbonyl ( CO ) ligand = 8 /2 = 4 .
In the
similar way, calculation of ligand numbers in iron carbonyl compound .
Atomic
number of Fe is 26 . The atomic number of the next inert gas is 36( Kr ).
The number
of electrons are contributed by the ligand due to formation of co-ordinate with
the central metal atom is ( 36 – 26 ) = 10 .
Now, each
ligand contributes two electrons in co-ordinate bond formation .
Hence, the
number of carbonyl ( CO ) ligand = 10 /2 = 5 .
Summary:
What is chelating effect in co-ordination
chemistry ?
What is EAN rule in co-ordination chemistry ?
Application of EAN rule in co-ordination chemistry .


No comments:
Post a Comment