What is ethane?
Ethane
is an organic compound with molecular formula C2H6. It is a saturated aliphatic
hydrocarbon. Ethane is colorless, odorless gas at standard pressure and temperature.
Ethane
is mixed with methane in natural gas. Again, a little ethane is also available
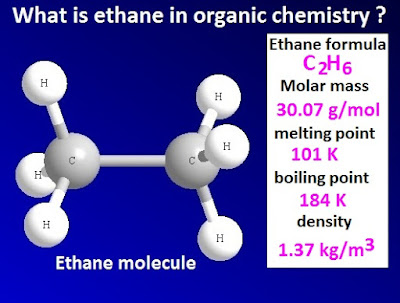
from coal gas. The melting point of ethane is 101K and the boiling point is
184K.
Ethane
is non polar saturated hydrocarbon. Consequently, it is insoluble or sparingly
soluble in water but readily soluble in organic solvents like benzene, ethanol
etc.
It burns in air oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water. Ethane is a saturated hydrocarbon and hence it is inert in nature. That is, it does not take part in a chemical reaction normally.
But
under certain condition it under goes chemical reactions, basically
substitution and oxidation reactions. However, ethane is an important gaseous
fuel.
When cooled to normal pressure, ethane gas becomes like a plastic crystal.Under this condition, the positions of hydrogenatoms are not fixed and the molecules rotate freely around the long axis.
Read more: Is methane a greenhouse gas?
What is the structure and formula of ethane?
The
chemical formula of ethane is C2H6. The exact molar mass of ethane is 30.07 g /
mol. In ethane molecule, two carbon atoms are attached to each other.
Each carbon atoms of ethane contain three hydrogen atoms. Each carbon atoms are sp3 hybridized.
The
H – C – C bond angle of ethane is 112ᵒ. The
C – C and C –H bond angle in ethane are 1.54Å, 1.09Å respectively.
Synthesis of ethane
There
are different methods for synthesis of ethane. Out of these, some important
methods are discussed below.
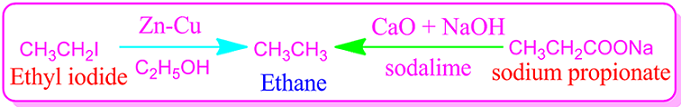
(I)Ethane
is synthesized by reduction of ethyl iodide or ethyl bromide using Zinc-Copper
couple in the presence of ethanol solvent.
(I)Decarboxylation
method: Ethane is also prepared by heating a mixture of anhydrous sodium
propionate and sodalime. This method is known as Decarboxylation method.
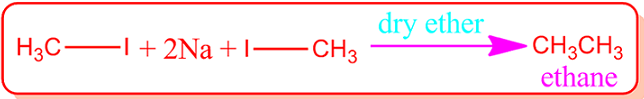
(III)Wurtz
reaction: It is an important reaction for the preparation of ethane. In this
case, methyl iodide and metallic sodium is heated in presence of dry ether
solvent.
(IV)Another
method for preparation of ethane is the reduction of alkene or alkyne in
presence of metal catalyst. It is industrial method for ethane gas preparation.
In
this case, ethylene or acetylene and hydrogen mixture is passed over a Ni
catalyst at 250ᵒC - 300ᵒC temperature.
Why is ethane used for?
Uses of ethane
There
are different uses of ethane gas. Ethane is mainly used as a fuel. It is also
used in the photochemical industry as a fraction of that produced in the
natural gas liquids plants alone.
Again,
ethylene gas that produced from ethane is used to ripening fruit. It is used as
the most specific volatile marker for the investigation of lipid per-oxidation.
Ethane
can be used as a refrigerant in cryogenic refrigeration systems. On a much
smaller scale, in scientific research, liquid ethane is used to vitrify
water-rich samples for electron microscopy.
A
thin film of water quickly immersed in liquid ethane at 123K or colder, freezes
too quickly for water to crystallize.
Slower
freezing methods can generate cubic ice crystals that can disrupt soft
structures by damaging the samples and reduced image quality by scattering the
electron beam before it can reach the detector.
Besides
these, ethane is used to prepare ethanol, ethyl halide, acetaldehyde, acetic
acid etc.
Why is ethane inert in nature?
Generally
ethane is an inert compound. It does not react easily with acids, alkalis, oxidants
or reductant. However, under suitable conditions, ethane
forms compounds by substitution reaction.
The cause of ethane
inactivity:
The
activity of any compound depends on four basic characteristics or conditions of
that substance.
These
characteristics or conditions are the presence of polar pi bonds in the
compound, the presence of one or more lone pair of electron, the presence of an
atom that can cause the expansion of the octet and the presence of an atom with
an incomplete octet.
Ethane
does not have any of the above characteristics. Consequently, ethane is inert
substance.
- What is ethane?
- What is the structure and formula of ethane?
- Synthesis of ethane
- Why is ethane used for?
- Why is ethane inert in nature?




No comments:
Post a Comment